Command-Line EDI Converter Documentation
The tool converts 837 and 835 transactions into JSON or comma-separated values (CSV) format.
The output is easy to understand and requires no EDI knowledge.
You can see examples of the CSV output here
To see examples of JSON output, navigate to any claim or payment example and click on “JSON” button.
For JSON conversions, the converter supports JSON Lines format with line-separated JSON objects. This provided an alternative to well-formed JSON with enclosing arrays, which are inefficient with large files.
This option is recommended for converting EDI files with many transactions and streaming.
The conversion is performed locally on your machine; your data never leaves your network.
The converter’s only dependency is Java. It supports any Windows, Linux, or macOS OS that can run Java 17 or higher.
Installation Instructions
- Download and install Java. You can also install OpenJDK using a package manager on Linux or macOS. Java 17 or higher is required. Once you install Java, verify the Java’s version using
java -versioncommand. - Download the converter (as a zip file) from this link
- Unzip the converter’s zip file
- Add the “bin” directory of the distribution to the path, e.g.,
export PATH=$PATH:ediconvert-2.6.2/bin. On Windows, go to “Advanced system settings”, “Advanced” tab, click “Environment Variables…”, click variable called “Path” and click “Edit…”. Append;ediconvert-2.6.2\binto the path.
You need a license key to run the converter. Request your trial license key by submitting this form:
Your license file will be named edi-license-<your org>.bin. Save this file anywhere and define the environment variable EDI_LICENSE with the path to the license file.
For example:
export EDI_LICENSE=edi-license.bin
set EDI_LICENSE=edi-license.bin
Run ediconvert -V to view the license information.
Running the Converter
To run the converter, simply provide a path to the EDI file and the output directory. The output directory must exist. Otherwise, the converter assumes that the value of the -o option is the file name:
mkdir json
./ediconvert edi/837/my_edi_file.edi -o json
You can also supply patterns to convert multiple files in one go:
./ediconvert edi/837 -p "*.edi" -o json
If you provide a directory for the output, the converter will convert each file from the input into this directory. If the output is a file, the converter converts all EDI files into one.
CSV mode always converts multiple files into a single output:
./ediconvert edi/835/ -p "*" -o csv/combined-835 -m csv
CSV Conversion
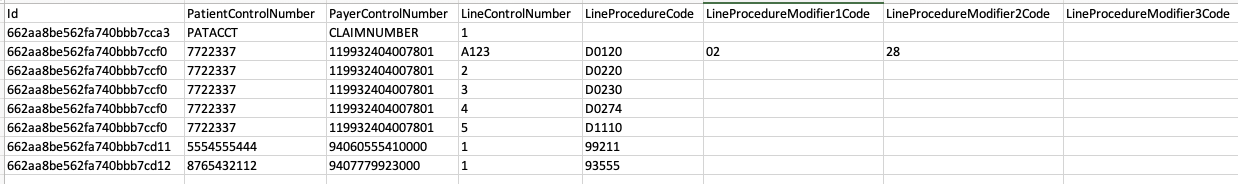
By default, the converter creates two output files, one for header-level data (claim or payment) and one for line-level data.
The internally generated ID, the patient control number, and the payer control number (for 835) fields are repeated for each line:
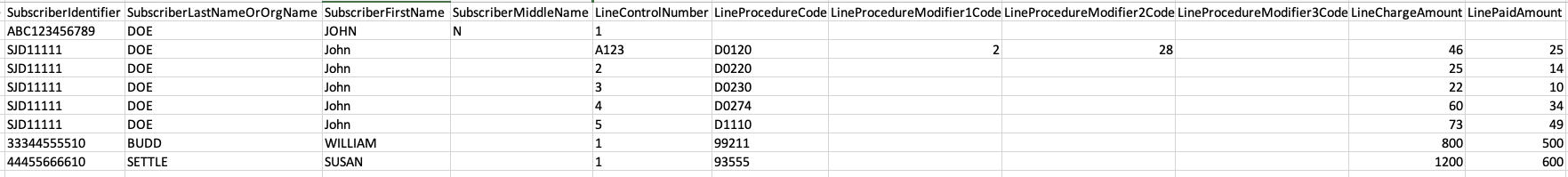
You can produce a single file using the --single-csv option. In this case, the converter will duplicate the header-level data for every line:
Converting to Standard Out
You can run the converter in the JSON Lines or in the CSV mode and pipe its output to another process, e.g.:
./ediconvert edi/837/my_edi_file.edi -m jsonl | grep '"zipCode":"37232"'
Note that the “regular” JSON conversion happens entirely in memory since the resulting output must be a well-formed JSON array. This may not work for large files containing many transactions.
CLI Options
Usage: ediconvert [-hrV] [--format-json] [--single-csv]
[--chunk-size=<chunkSize>] [-m=<outputFormat>] [-o=<outFile>]
[-p=<filePatterns>] <ediFileOrDir>
Converts X12 EDI files to JSON or CSV
<ediFileOrDir> EDI file or a directory containing EDI files
-p, --patterns=<filePatterns>
File patterns to match in the directory, e.g., '*.edi'.
Required if ediFileOrDir is a directory
-r, --recurse Recursively search for matching files in all
subdirectories
-o, --out=<outFile> Output file or directory. Defaults to the name of the
EDI file + the extension depending on the output
format;'.json', '.jsonl' or '.csv'. If omitted, the
converted will write to standard out, which can be
used for piping/streaming the output.
-m, --mode=<outputFormat>
Output format. Acceptable values: JSON, JSONL, CSV.
Defaults to JSON
--format-json Format JSON with indentation and new lines. Ignored for
CSV and JSONL.
--single-csv Convert into a single CSV file with header data
repeated for each line. By default, service
line-level fields are saved into a separate file.
Ignored for non-CSV modes
--chunk-size=<chunkSize>
How many transactions to parse and convert at once.
This option determines the memory footprint and can
be used for fine-tuning. Ignored for JSON mode.
Defaults to 100
-h, --help Show this help message and exit.
-V, --version Print version information and exit.
Logging
The converter creates logs with information and diagnostic messages in the “logs” directory. These logs are useful when routing the output to standard out.
The default location of the logs folder is the directory where the converter is executed. It can be changed by defining the ediconvert_logs_dir environment variable, e.g.,
export ediconvert_logs_dir=ediconverter_logs